By Tim Lambert
Dedicated to Yvonne Shaw
For rich Tudors fashion was important. Their clothes were very elaborate. For the poor clothes had to be tough and practical. All classes wore wool. However, it varied in quality. The rich wore fine-quality wool. The poor wore coarse wool.
The Tudors used linen to make shirts and underwear. Only the rich could afford silk clothes. Rich Tudors also embroidered their clothes with silk, gold, or silver thread. Rich Tudor women wore silk stockings.
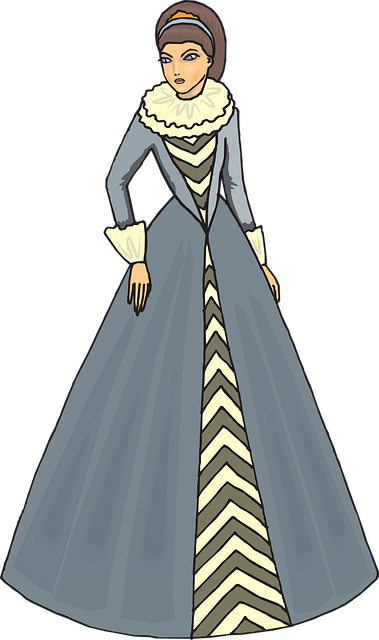
Tudor men wore short trouser-like garments called breeches. They also wore tight-fitting jackets called doublets. Another jacket called a jerkin was worn over the doublet. Over the jerkin, rich men wore a gown, or later in the 16th century a cloak or cape.
However, instead of a doublet, many workingmen wore a loose tunic. It was easier to work in. Some workingmen wore a leather jerkin called a buff-jerkin. Men also wore stockings or woolen socks, which were called hose.
Under their dresses, Tudor women wore a garment like a nightie called a shift or chemise. It was made of linen or wool. A linen or wool dress went over it. A woman’s dress was made of two parts, a bodice or corset-like garment and a skirt. Sleeves were held on with laces and could be detached. Working women wore linen aprons.
In the late 16th century many women wore a frame made of whalebone or wood under their dress called a farthingale. If they could not afford a farthingale women wore a padded roll around their waist called a bum roll.
In the 16th century, women did not wear knickers. However, Tudor men sometimes wore linen shorts as underwear.
All Tudors wore hats. Poor women often wore a linen cap called a coif. After 1572 by law all men except nobles had to wear a woolen cap on Sundays.
In the 16th century, buttons were usually for decoration. Clothes were often held together with laces or pins. Furs in Tudor times included cats, rabbits, beavers, bears, badgers, and polecats.
Tudor Dyes
The Tudors used mostly vegetable dyes such as madder for red, woad for blue, or walnut for brown. However, you have to use a chemical called a mordant to fix the dye. The mordant changed the color of the dye e.g. a plant called weld was used with alum for yellow but if used with iron or tin it produced shades of green.
The most expensive dyes were bright red, purple, and indigo. Poor people often wore brown, yellow, or blue. Incidentally in the 16th century scarlet was not a colour it was the name of fine, expensive wool.
It is a myth that in Tudor times people were very dirty and smelly. Most people tried to keep themselves clean but it was difficult to keep free of vermin. On the wreck of the Mary Rose, many lice combs were found. A bone ear scoop and a bone manicure set were also found.